The most common cause of a data breach—aside from the threat actors themselves—is human error.
That’s just one of many data breach statistics that reveal how challenging and dynamic data breaches are as a cyber threat. From common causes to impacts and motivations, continue reading to learn the who, what, and why of data breaches.
Table of contents
-
Top data breach statistics
-
Impact and cost of a data breach
-
Frequency and common causes of data breaches
-
Data breach statistics by industry
-
Types of data most commonly compromised
-
Most common types of data breaches and attack vectors
-
Data breach trends
-
Data breach response statistics
-
How to protect against data breaches
-
Stop data breaches before they start
-
FAQ
Key takeaways
|
Top data breach statistics
The Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) defines a data breach as “when unauthorized individuals access and/or remove personal information from the place where it is stored.” Basically, it’s when any type of data is accessed by someone who is not meant to access it, often for malicious purposes.
Recent data breaches have shown us how threat actors are getting more creative with how they access information. They’re using tried-and-true methods of access, like malware and phishing, with AI tools to make their jobs easier. Below are key cybersecurity statistics that show the state of data breaches in 2025.
-
Data breaches, or unauthorized access to data, are among the top concerns of IT professionals in remote work environments. (Huntress)
-
Data breaches often span multiple environments, with 40% involving data stored across various platforms. (IBM)
-
2023 was a record-breaking year for reported data compromises, with 3,205. 2024 was similar, with 3,158. However, the number of victim notices went up exponentially, by 211%, with 1.3 billion notices going out in 2024. (ITRC)
-
This means that approximately six victim notices went out for every adult in the United States. (ITRC)
-
But if you were to exclude the top five mega-breaches of 2024, there was actually a 47% decrease in the number of victim notices sent out. (ITRC)
-
The Ticketmaster attack, which threat actors claim compromised 560 million individuals, was the largest data breach of 2024. (ITRC)
Impact and cost of a data breach
Data breaches have both short- and long-term effects. Downtime and lost data can have massive financial impacts on the organization. For the end user, that lost data isn’t just a major inconvenience and invasion of privacy, but can also be a financial blow and even lead to stolen identities.
That’s not something that just goes away, either. Any negative impact on your credit score generally lasts at least seven years. And while we mostly talk about the financial impact of data breaches and other cyberattacks, there’s no doubt an implied emotional component is there, too.
-
The average cost of a data breach in the United States from 2006 to 2024 was nearly $9.5 million. (Statista)
-
Data recovery (81%), data breaches (80%), and ransomware (63%) are among the most commonly covered types of cyber events in insurance policies. (Huntress)
-
For 27% of organizations, cyberattacks cost between $100,001–$500,000 per year. (Huntress)
-
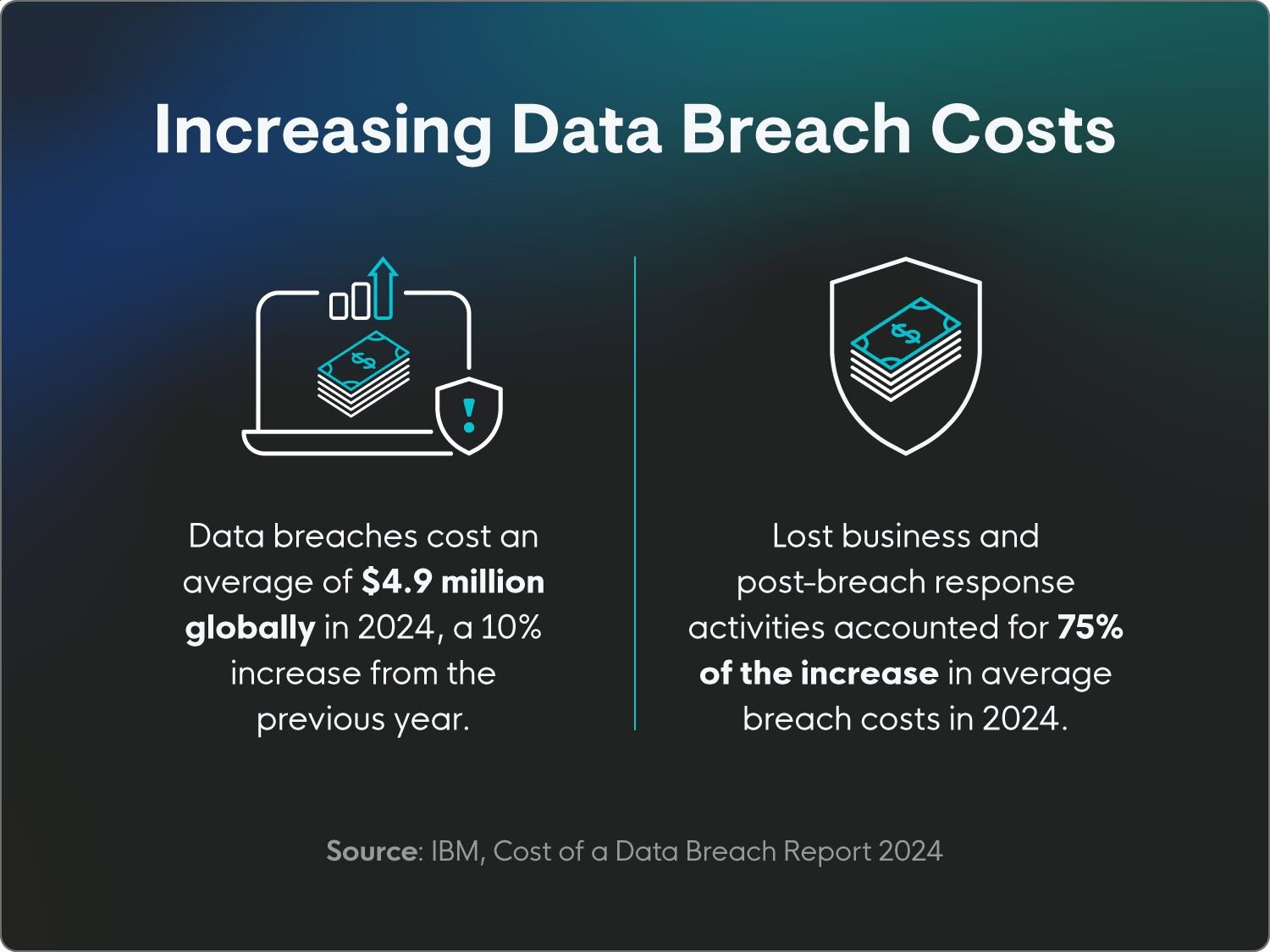
Data breaches cost an average of $4.9 million globally in 2024, which marked a 10% increase from the previous year. (IBM)
-
The highest breach cost was from data stored publicly, incurring $5.17 million in average costs. (IBM)
-
Lost business and post-breach response activities accounted for 75% of the increase in average breach costs in 2024. (IBM)
-
Stolen credit card data sells on the dark web for an average of $10 to $110. (Privacy Affairs)
-
Stolen banking and business account data can sell for an average of $10 to $4,255. (Privacy Affairs)
-
Compromised crypto account data is a hot-ticket item, selling on the dark web for an average of $20 to $2,650. (Privacy Affairs)
-
Forged documents like IDs and passports are super valuable on the dark web, selling for an average of $150 to $4,000. (Privacy Affairs)
-
As far as the actual cost to pay for a data breach? Low-quality, low-success malware attacks can cost about $35, whereas a high-quality, high-success attack can make $4,500 per 1,000 accounts breached. (Privacy Affairs)
-
The median amount organizations ended up paying in ransomware breaches went down more than 23% from $150,000 in 2024 to $115,000 in 2025. (Verizon)
-
In 2025, 64% of organizations that experienced ransomware attacks didn't pay the ransom, up from 50% in 2023. (Verizon)
Learn more about the true costs of cybercrimes and arm yourself with insights to protect your data.
Data breach frequency and common causes
How common are data breaches? They’re happening more and more, so let’s start there.
While human error is one of the most common causes of data breaches, the threat landscape is also changing fast. Even if the average person were better about following cybersecurity best practices to reduce their attack surface, the way threats are developing would have them constantly playing catch-up.
More than that, though, threat actors are persistent. Here are some common causes of data breaches.
-
Poor password management or using common passwords is a big concern for both in-person and remote teams, with 28% of IT professionals saying they think it’s the worst habit of remote and hybrid employees. That’s ahead of things like opening obvious phishing scams and not using a secure network. (Huntress)
-
About 9% of IT professionals feel that their organization’s data loss prevention measures are underfunded or underresourced. (Huntress)
-
It’s estimated that nearly all data breaches (95%) can be blamed on human error, such as poor cyber hygiene and falling for phishing attacks. (Mimecast)
-
Basic web application attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) were the cause of 12% of data breaches in 2025, up 3% from 2024. (Verizon)
-
60% of data breaches in 2025 involve a human element, like malicious insiders or falling for phishing scams. It’s worth noting that other types of data breaches often involve human factors like a lack of education around cybersecurity best practices and policies; however, in this instance, the human element is the direct cause. (Verizon)
-
Of those data breaches that included a human element, 32% involved credential abuse, 23% social actions, 14% errors, and 7% malware. (Verizon)
-
30% of data breaches in 2025 involved a third party, which includes device vulnerabilities. (Verizon)
-
17% of data breaches in 2025 were espionage-motivated. (Verizon)
-
46% of enterprise-level compromised systems were unmanaged, hosting both professional and personal credentials. (Verizon)
-
Generative AI platforms like ChatGPT and Gemini pose a potential risk to organizations, with 72% of employees using their personal emails on the platforms for work, meaning sensitive data is potentially being compromised. (Verizon)
-
89% of internal data breaches are motivated by financial gain. (Verizon)
-
Miscellaneous errors or innocent mistakes accounted for 12% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
The top types of miscellaneous errors were misdelivery (49%), misconfiguration (30%), and publishing errors (9%). (Verizon)
Data breach statistics by industry
Data breaches can happen in any industry and to anyone. But standout industry targets like healthcare and education have particularly sensitive data that threat actors want. Below is an overview of how data breaches impact different industries.
Healthcare data breaches
Cybersecurity threats in healthcare are massive, both in their impact and frequency. Healthcare accounts for many of the biggest attacks each year, compromising millions of people’s personal data. Here’s an overview of healthcare cybersecurity threat statistics.
-
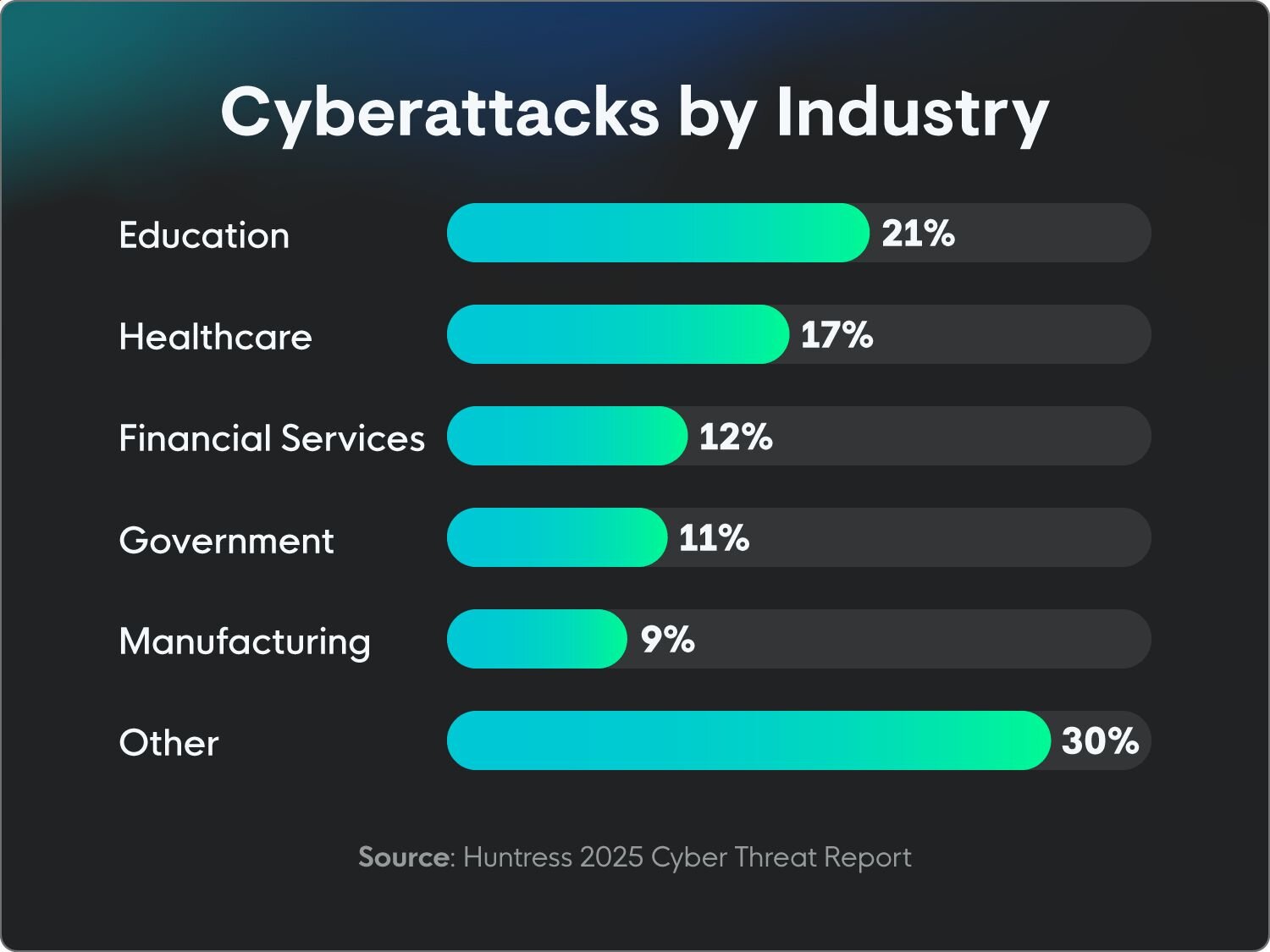
17% of all attacks in 2024 were in healthcare. (Huntress)
-
A third of cybersecurity professionals in healthcare rate data breaches as the most common cyber threat. (Huntress)
-
Phishing attacks are the most common type of breach, with 40% of healthcare organizations experiencing them in the past year, followed by data breaches at 20%. (Huntress)
-
Disruption of patient care is the biggest concern for healthcare IT professionals, with 52% rating it as the most significant impact cyber threats have on their organization. (Huntress)
-
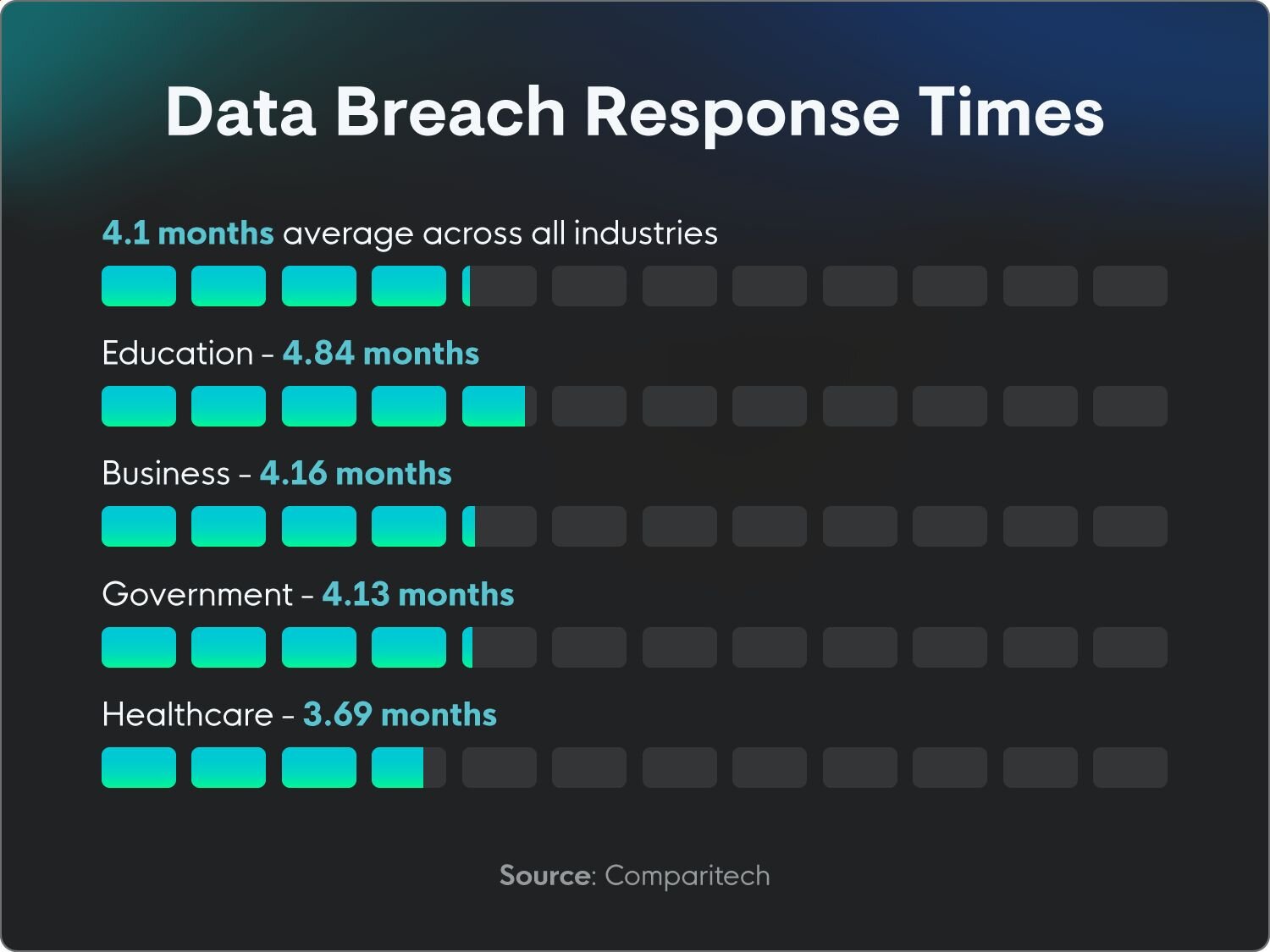
It takes an average of 3.69 months to report data breaches in healthcare, the shortest industry average. (Comparitech)
-
The largest healthcare incident so far in 2025 is the Yale New Haven Health System attack, which compromised 5.56 million individuals' data in April. (US Department of Health and Human Services)
-
The biggest healthcare data breach of all time was the Change Healthcare incident in 2024, which impacted 190 million individuals. (HIPAA Journal)
-
On average, 758,288 records per day were breached in 2024. (HIPAA Journal)
-
Hacking is the leading cause of healthcare cyber incidents. (HIPAA Journal)
-
The cost of a data breach in healthcare is higher than the average cost of breaches overall, at $9.77 million. (IBM)
-
Healthcare experienced 536 reported compromises in 2024. (ITRC)
Data breaches in education
Similar to healthcare, education is another top target for threat actors. Schools store a stockpile of personal information that attackers are eager to access for various reasons, like selling it on the dark web or ransoming it for money.
Here is an overview of data breaches in education:
-
Education is one of the most commonly targeted industries, with 21% of attacks in 2024. (Huntress)
-
Education experienced 162 reported compromises in 2024. (ITRC)
-
A lesson learned the hard way: Education has the longest reporting time, taking an average of 4.84 months to report data breaches. (Comparitech)
-
62% of data breaches in education are by external threat actors, with 59% of those being organized crime groups. (Verizon)
Manufacturing data breaches
While data breaches in manufacturing are slightly less common than some in other industries, they do have a significant impact on operations. Because manufacturing processes are so interconnected, often involving highly specialized machinery with systems that rely on one another, even a minor disruption can snowball into major delays, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Below are some manufacturing data breach stats.
-
9% of all attacks in 2024 were in manufacturing. (Huntress)
-
The cost of data breaches in the industrial sector increased 18% in 2024 to $5.56 million, which was 13% more than the overall average. (IBM)
-
Manufacturing experienced 317 reported compromises in 2024. (ITRC)
-
Manufacturing organizations are especially impacted by the costs of a data breach, with downtime costing thousands of dollars. For example, an automotive manufacturer may lose more than $22,000 for every minute of downtime. (Forbes)
-
Manufacturing accounts for 28% of denial-of-service (DOS) attacks. (Verizon)
Financial Services data breaches
Naturally, financial information is a primary target for threat actors. As we mentioned earlier, financial data can be worth hundreds or even thousands of dollars on the dark web. Here are some top financial services statistics.
-
Financial services experienced 737 reported compromises in 2024, making it the top-attacked industry, knocking healthcare out of first place for the first time since 2018. (ITRC)
-
The main cause of the increased attacks in the financial sector was a rising number of attacks in commercial banking and insurance. (ITRC)
-
The finance sector accounts for 35% of DOS attacks. (Verizon)
State and local government data breaches
With a lot of sensitive information—and despite strict compliance regulations—state and local governments aren’t immune to data breaches. Here’s an overview of some of the findings for government data breaches in 2024 and 2025.
-
11% of all reported attacks in 2024 were in the government. (Huntress)
-
Government agencies take an average of 4.13 months to report data breaches. (Comparitech)
-
Government IDs were compromised in 22% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
Three-quarters of ransomware attacks in government are state, local, tribal, or territorial (SLTT). (Verizon)
Types of data most commonly compromised
Data breaches frequently expose personally identifiable information (PII), like names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and dates of birth, which are highly sought after for identity theft. Beyond individual information, corporate intellectual property and sensitive internal documents are often compromised, leading to major business disruption and competitive disadvantages.
Here’s an overview of the most commonly compromised types of data:
-
1 in 3 data breaches involve shadow data, or data created without an organization's knowledge, such as an employee saving work emails to their personal account or creating copies of sensitive information. This data goes unaccounted for by IT teams when there’s a breach, because they don’t know it exists. (IBM)
-
84% of compromised data in 2024 was classified as sensitive data, like financial or medical information. (ITRC)
-
Passkeys are the key to prevention, particularly in breaches that involve stolen credentials. Some believe that the majority of stolen credential breaches in 2024 could’ve been avoided if organizations had made passkeys mandatory. (ITRC)
-
More than 2.8 billion passwords were posted on criminal forums in 2024. (Verizon)
-
Emails were compromised in 61% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
Phone numbers were compromised in 39% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
Passwords were compromised in 28% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
IP addresses were compromised in 13% of data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
Most common types of data breaches and attack vectors
Bad actors use many different types of attack vectors, or methods of entry, to get access to systems. The findings below summarize the most common types of data breaches and their attack vectors.
-
Healthcare and education made up 38% of all attacks in 2024. (Huntress)
-
In 2025 so far, 53% of organizations have experienced malware infections. (Huntress)
-
Cyberattacks were the main cause of most data breaches in 2024, but only 30% of notices actually included information about the attack vector. (ITRC)
-
53% of data breaches in 2025 were classified as system intrusion, compared to only 36% in 2024. (Verizon)
-
Social engineering accounted for 17% of data breaches in 2025, down from 22% in 2024. (Verizon)
-
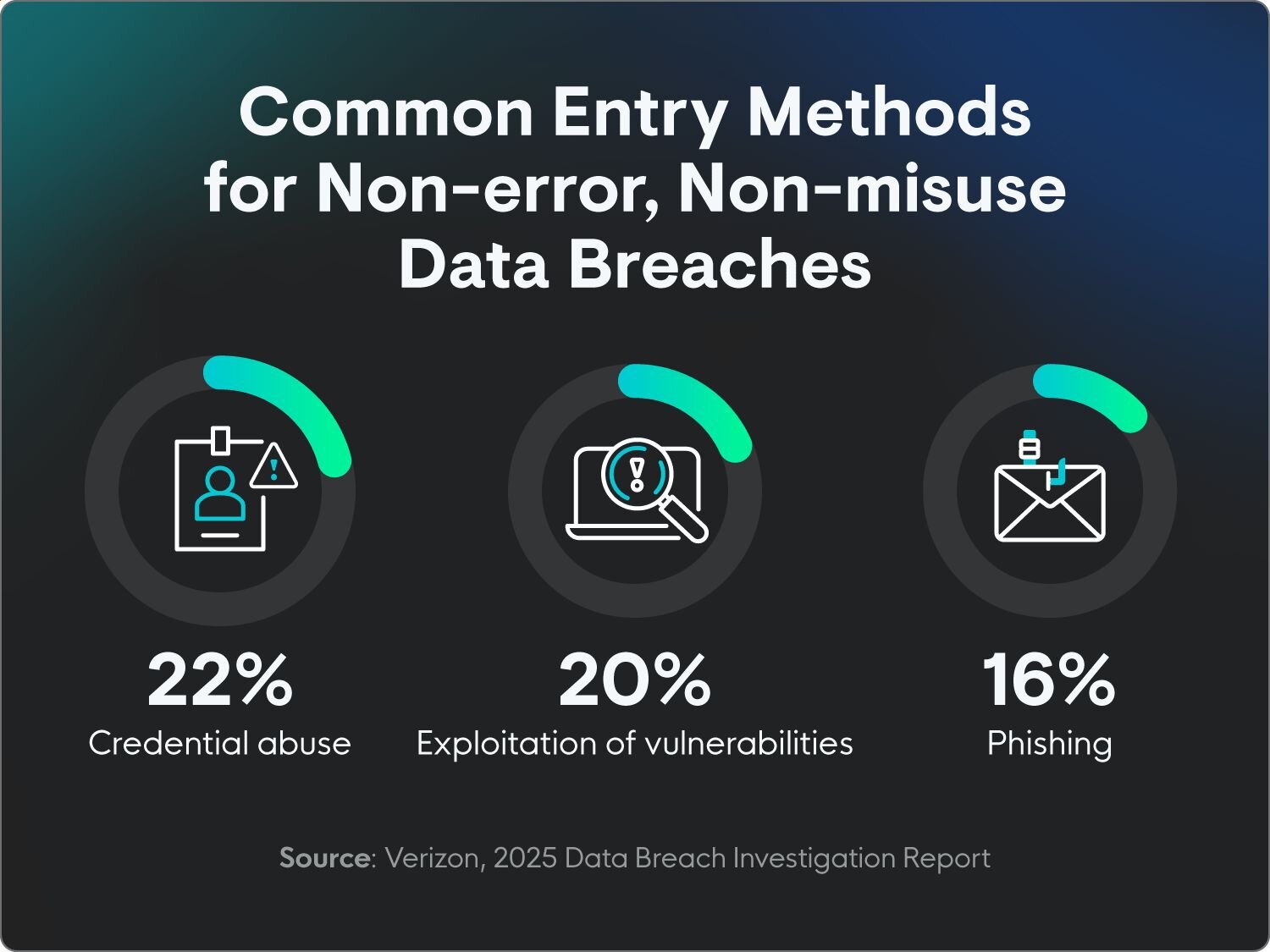
Credential abuse was the initial access vector in 22% of non-error, non-misuse breaches, where human errors weren’t the main cause, in 2025. Credential abuse as an access vector can be linked to an increased use of zero-day exploits targeting VPNs and edge devices. (Verizon)
-
Exploitation of vulnerabilities was the initial access vector in 20% of non-error, non-misuse breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
Phishing was the initial access vector in 16% of non-error, non-misuse breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
Data breach trends
While there are consistencies year-over-year when it comes to data breaches like the human aspect of breaches and financial motivations, things also change. A major trend in 2025 is the rise in breaches involving cloud environments and shadow data. Below is an overview of some of the data breach trends this year.
-
More than 3 of 4 remote access incidents involved remote access trojans (RATs) in 2024. (Huntress)
-
Almost a quarter (24%) of IT professionals rate cloud security breaches as one of the emerging threats they’re most concerned about. (Huntress)
-
Infostealers were responsible for nearly a quarter (24%) of threats in 2024. (Huntress)
-
Financial gain (27%) and data theft (23%) are considered the most common motivations for threat actors. (Huntress)
-
Ransomware was present in 44% of all data breaches in 2025, up from 32% in 2024. (Verizon)
-
Ransomware impacts smaller organizations more than larger ones. It was used in 39% of data breaches on large organizations but only 88% of breaches on non-enterprise businesses. (Verizon)
Data breach response statistics
Data breach response matters almost as much as prevention. Here’s an overview of some stats that show how long reporting takes and how managed security support can improve data breach outcomes.
-
On average, it takes organizations 4.1 months to report a data breach after ransomware attacks. (Comparitech)
-
The average savings for those who use automated detection and response is $2.2 million. (IBM)
-
Organizations within designated industries, such as finance and government sectors, are required to report data breaches and other cyber incidents to Homeland Security within 72 hours. (CISA)
-
Each US state also has its own response and reporting laws that organizations must follow. (CISA)
-
Data breach reporting periods averaged 3.9 months in states with specific reporting timeframes, compared to 4.2 months in states without the same regulations. (Comparitech)
-
Only about 54% of edge device vulnerabilities were properly dealt with this year, taking a median time of 32 days. (Verizon)
-
Infrastructure monitoring, like managed endpoint detection and response (EDR), was responsible for detecting 18% of all non-threat-actor-disclosed data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
-
Employees were responsible for reporting 14% of all non-threat-actor-disclosed data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
- And on the other side of the coin, customers were responsible for reporting 10% of non-threat-actor-disclosed data breaches in 2025. (Verizon)
How to protect against data breaches
Proactive measures are important in preventing data breaches. Here are our tips for protecting your personal and organizational data from data breaches and other cyberattacks.
-
Perform regular updates and audits: Evaluate cybersecurity measures at regular intervals to make sure there are no potential vulnerabilities and all systems are compliant.
-
Invest in EDR: EDR solutions give you continuous monitoring and analysis of endpoint activities for rapid detection, investigation, and automated response to sophisticated cyber threats that traditional antivirus solutions might miss. This visibility and quick containment minimize the impact of attacks, reduce response times, and help maintain business continuity.
-
Train employees: Human error is a major factor in data breaches. Conduct regular security awareness training for all employees, focusing on spotting phishing attempts, recognizing social engineering tactics, secure data handling practices, and reporting suspicious activity.
-
Use passkeys: Passkeys shift the security burden away from easily compromised human memory and vulnerable server-side password storage, placing it firmly on secure, device-based authentication. This reduces the impact and likelihood of breaches stemming from stolen or phished credentials.
-
Implement least privilege: Adhere to the principle of least privilege, where individuals only have access to the data and systems absolutely necessary for their role. Regularly review and revoke access as roles change or employees leave.
-
Have an incident response plan: In the event of a data breach, it’s important to have an incident response plan already in place. This includes steps for assessing damage, locking down and backing up accounts, and reporting through the proper channels, such as to the Internal Crime Complaint Center.
Stop data breaches before they start
The data breach statistics we’ve shared here show how frequently and why data breaches happen so you have a clearer picture of where many organizations may be falling short. While it can be scary to see the sheer number of breaches happening every year, there’s a lot that businesses and individuals can do to help prevent them.
Threats can seem overwhelming, but with our in-depth understanding of how threat actors think, we know what to look for. Huntress gives you fully managed EDR, so you've got 24/7 support from security experts ready to respond to threats.
FAQ
Are 90% of data breaches caused by human error?
Closer to 95% of all data breaches can be pinned on human error.
How many data breaches are there each year?
According to the ITRC, there were 3,158 reported data compromises in 2024.
What are the odds of a data breach?
The odds of experiencing a data breach are quite high, but you can reduce your risk by implementing cybersecurity measures like multi-factor authentication and passkeys.
What is the #1 cause of data breaches?
Human error is the main cause of data breaches.