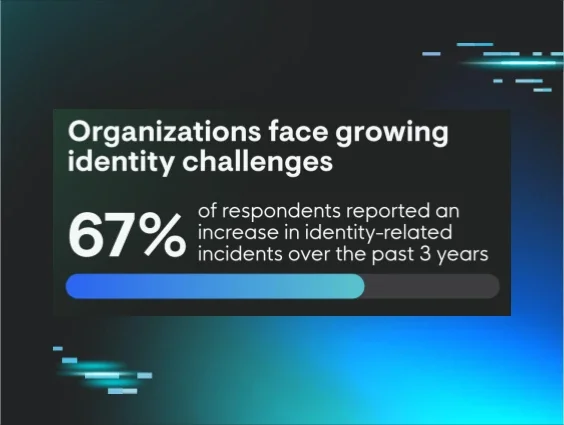
What is identity abuse in cybersecurity?
Identity abuse occurs when digital or physical identities are manipulated or exploited without authorization to gain illicit access to systems, data, or resources. This could involve stolen credentials, fraudulent activities, or impersonation — all with the intent to compromise security or commit crimes.
What does identity abuse look like?
Identity abuse covers a wide range of malicious activities that undermine both personal and organizational security. It’s not just about stolen passwords; attackers are finding creative new ways to weaponize identities. Here’s a closer look at some common forms of identity abuse:
Credential Theft and Exploitation Hackers often use phishing, malware, or methods like credential stuffing (reusing stolen passwords across platforms) to steal usernames and passwords. These are then used to access accounts and wreak havoc.
Account Takeover (ATO) ATO involves attackers seizing full control of user accounts after obtaining their credentials. This allows them to steal sensitive data, execute additional attacks, or disrupt operations.
Abuse of Over-Permissioned Identities Service accounts or identities with excessive permissions are prime targets. By abusing these, attackers gain long-term access and can move laterally within an organization’s network.
Misuse of Identity Federation Systems Compromising identity federation setups (e.g., Single Sign-On systems) allows attackers to manipulate permissions, grant rogue access to domains, and infiltrate protected services.
Identity-Based Disinformation At a larger scale, identities can be weaponized to spread false or harmful messages online, aiming to fuel social or political unrest.
Examples Beyond Cybersecurity
Identity abuse doesn’t stop at digital crime. Here are some offline examples that show how identities can be misused in broader contexts:
Financial Identity Theft Stealing someone’s financial information to commit crimes like opening fraudulent credit lines or making unauthorized purchases.
Medical Identity Theft Using stolen insurance details to get medical treatments or prescription drugs is another form of identity abuse that can have devastating consequences.
Criminal Identity Theft Imagine being falsely implicated in a crime because someone used your name when arrested. This type of identity theft can destroy reputations and take years to resolve.
Why does identity abuse matter in cybersecurity?
At its core, identity abuse is about exploiting trust. Whether it’s a hacker gaining access to sensitive systems or someone impersonating you in a fraud scheme, the repercussions can be severe. For businesses, identity abuse can lead to costly data breaches, tarnished reputations, and regulatory penalties. On a personal level, it can cause financial ruin and emotional distress.
The shift towards cloud-based systems, remote work, and digital identities has only made securing identities more critical. Understanding identity abuse is the first step toward staying one step ahead of attackers.
Protecting your business against identity abuse?
Staying safe means staying proactive. Here are some best practices to combat identity abuse:
Strong Password Practices Use unique, complex passwords for every account. Better yet, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add another layer of protection.
Monitor Privileged Accounts Regularly review and limit permissions on accounts to ensure they have access to only what’s necessary.
Invest in Identity Management Tools Use tools that help organizations manage identities securely, such as identity and access management (IAM) systems.
Stay Aware of Threat Patterns Keep up with cybersecurity trends, and train staff to recognize threats like phishing scams.
Key takeaways
Identity abuse is a serious threat that spans digital and physical domains. Common methods include credential theft, account takeovers, and misuse of privileged access.The consequences affect businesses and individuals — from data breaches to fraud and beyond. Protecting against identity abuse requires robust passwords, permission controls, and constant vigilance.


Protect What Matters