Many common passwords can take a threat actor only minutes or even seconds to hack.
That’s why having multiple layers of protection, including a strong password, is essential. One of these methods should be multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires multiple verification steps to help slow down or prevent unauthorized access.
Learn more about what multi-factor authentication is, why it’s important, and how to set it up at your organization.
What is MFA?
MFA is an essential cybersecurity process that requires users to verify their identity multiple times (at least twice, but it can be three or more times) to access a resource like an application, online account, or VPN. Instead of just a single password, MFA calls for a combination of different types of authentication methods, which are typically categorized into three groups
-
Something you know, like a password or PIN
-
Something you have, like a smartphone or a hardware token
-
Something you are, like a fingerprint or facial scan
Why is MFA important?
The primary purpose of MFA is to create a layered defense, making it more difficult for an unauthorized user to access an account. Even if a threat actor manages to steal your password (something you know), they would still need the second factor—like your phone (something you have)—to successfully log in. Benefits of MFA include:
-
Enhanced security: MFA significantly increases protection by requiring more than just a password, making it much harder for threat actors to access accounts even if they steal login credentials.
-
Faster response time: MFA stops most password attacks at authentication, preventing breaches and saving security teams time and resources.
-
Reduced risk of data breaches: By creating a strong barrier against unauthorized access, MFA drastically lowers the likelihood of account takeovers and the theft of sensitive data through methods such as credential stuffing.
-
Regulatory compliance: Implementing MFA helps organizations meet strict security requirements for regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, avoiding potential fines and legal issues.
-
Secure remote access: It enables employees to securely access company networks and resources from anywhere, supporting a flexible and safe remote work environment.
-
User-friendly options: Modern MFA methods, such as push notifications and biometric scans, offer strong security with minimal friction, making them easy and quick for users to adopt.
How does MFA work?
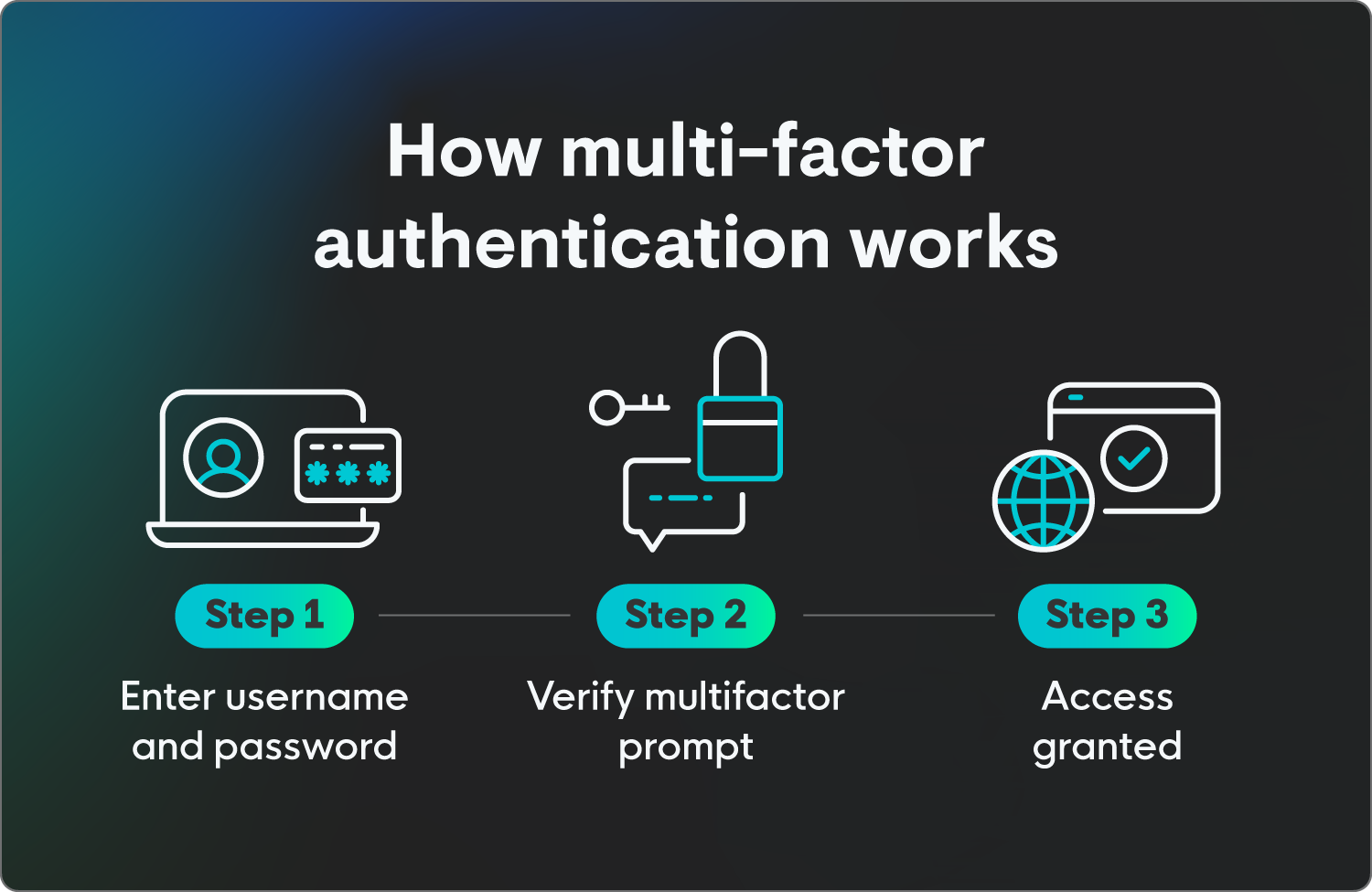
Multi-factor authentication is a pretty straightforward process where the main steps include:
-
Initial login: The user starts by providing their first factor, usually a username and password (something they know).
-
MFA challenge: After the system successfully verifies the password, it doesn't give immediate access. Instead, it presents a challenge, requesting the second factor.
-
Second factor verification: The user must then provide the second form of authentication. For example, they might receive a one-time passcode (OTP) via a text message to their phone, get a push notification on an authenticator app, or be prompted to use a fingerprint scanner.
-
Access granted: Access to the account is granted only after all factors are successfully verified, proving that the user both knows the password and possesses the other factor. If an attacker has only the password, they’ll be blocked at the second step because they lack the required second factor. This makes it harder for a threat actor to compromise the account.
Types of multi-factor authentication
There are several common types of multi-factor authentication, each using a different verification category to enhance security. They’re used in combination with a password to create a strong defense. Here’s an overview of some of the most frequently used forms of MFA.
Authenticator apps
These apps, such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, generate a unique, time-sensitive code (a time-based one-time password, or TOTP) that users must enter to log in.
This method is generally considered more secure than SMS because the codes are generated locally on the device and don't rely on a cellular network that could be compromised.
SMS or text message codes
This is one of the most common and familiar types of MFA. After entering their password, a user receives a unique code via text message to their registered phone number. They then enter this code to complete the login process.
While convenient, it’s less secure than authenticator apps due to the risk of SIM swapping, which is when threat actors fraudulently transfer a victim’s number to a SIM controlled by them, and other cellular network vulnerabilities.
Biometrics
This method uses a unique physical characteristic of the user for verification, like fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or iris scans. This is often used on smartphones and other personal devices as a quick and highly secure way to authenticate.
Hardware security keys
These are physical devices, such as a YubiKey, that plug into a computer's USB port or connect wirelessly. To authenticate, a user simply presses a button on the key. This is one of the most secure forms of MFA because it’s resistant to phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Push notifications
A user receives a notification on their smartphone or other registered device, which they can approve or deny with a single tap. This user-friendly method removes the need to manually enter a code.
Real-world MFA examples
Let’s go over how these different types of MFA may play out. Here are some examples of how multi-factor authentication may happen in the real world:
-
Something you know: When logging into your Microsoft account, you’re prompted to enter the last four digits of your phone number as additional security.
-
Something you have: When signing into your work account from a new location, you’re sent a push notification to your work phone to verify your identity.
-
Something you are: When using your phone to check if a deposit has gone through in your banking app, you’re required to use a biometric signature to verify your identity, so you use the face scan feature on your iPhone to gain access.
AI's role in multi-factor authentication
AI's role in MFA is to make the process smarter, more seamless, and more secure by moving beyond static, rigid security checks. Instead of requiring a second factor every single time, AI-powered MFA uses machine learning to analyze user behavior and context in real time.
This lets the system assess the risk of a login attempt and either ask for an additional verification step or, in low-risk situations, give faster access. Essentially, AI helps MFA adapt to the specific situation, making it more effective and user-friendly.
How leaders can implement MFA
Implementing multi-factor authentication for businesses is a critical step in strengthening an organization's cybersecurity posture, but it requires more than simply flipping a switch. A successful rollout involves careful planning, clear communication, and a strategic approach to choosing the right technology.
Here are some tips and considerations for implementing MFA effectively:
-
Get buy-in: Before implementing MFA, explain to all staff why it’s important—from leadership to entry-level—as a crucial security measure protecting company and personal data.
-
Start with the most vulnerable accounts: Prioritize implementing MFA on accounts that have elevated privileges or access to sensitive data like administrator accounts, cloud service portals (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace), and financial systems. This approach can reduce the most critical risks right away.
-
Choose the right MFA method for you: While any form of MFA is better than none, certain methods offer stronger protection. Opt for authenticator apps or hardware security keys rather than SMS-based MFA, which, while convenient, is vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks.
-
Go for flexibility and scalability: Look for an MFA solution that can grow with your organization and supports various authentication methods. A solution that integrates seamlessly with your existing infrastructure (e.g., identity providers, VPNs) will make deployment and management much easier long term.
-
Develop a phased rollout plan: Avoid a company-wide all-at-once rollout, which can overwhelm IT support and users alike. Instead, implement MFA in phases, starting with a small pilot group or single department. Gather feedback, address any issues, and refine your process before expanding to the next group.
-
Provide clear and simple instructions: Create easy-to-follow, step-by-step guides and videos for users. Offer a help desk or a designated point of contact to help with any issues that come up during the setup process.
-
Use multiple forms of protection: Consider implementing various forms of cyber protection at login, such as SSO login, zero trust architecture, and MFA.
-
Plan for account recovery and lost devices: A critical part of MFA is having a secure process for when a user loses their phone or other second factor. Establish a clear, secure procedure for identity verification and account recovery that doesn't compromise security, including who to contact and how.
Multi-layered endpoint protection is within reach
Protecting your access points is one of the first steps of many to ensure threat actors are unable to access your data. Setting up systems like multi-factor authentication can help stop attacks from happening and alert team members to any potential password vulnerabilities.
We understand what threats like credential theft and unauthorized access mean for your business, and we’re here to help. Huntress has you covered continuously with managed identity threat detection and response (ITDR), protecting identities across your organization 24/7.
FAQ
What is the difference between 2FA and MFA?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a broader term for any security system that requires two or more authentication methods to verify a user's identity. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a specific type of MFA that requires exactly two authentication methods. While all 2FA is a form of MFA, not all MFA is 2FA, as MFA can involve three or more factors.
Do I need multi-factor authentication?
Yes, MFA is an important cybersecurity protection. Passwords alone aren’t enough to defend against modern cyber threats, as they can be easily stolen, guessed, or compromised in data breaches. MFA adds a critical second layer of security, making it significantly harder for threat actors to access your accounts even if they have your password.
How do I enable multi-factor authentication?
Navigate to the security or privacy section of your account (e.g., Google, Apple, Microsoft). From there, look for a setting labeled "Two-Factor Authentication," "Multi-Factor Authentication," or "Two-Step Verification."
After you select this option, you'll be guided through a setup process where you can choose your preferred second verification method, such as a code from an authenticator app (like Google or Microsoft Authenticator), a text message to your phone, or a security key. Using an authenticator app over text messages is highly recommended for enhanced security.