How phishing has evolved over time
From obvious scams to sophisticated attacks
Remember those laughably bad phishing emails from the early 2000s? The ones riddled with typos, claiming you'd inherited millions from distant relatives, or offering miracle weight loss solutions? Those amateur-hour attempts were easy to spot and dismiss, and delete.
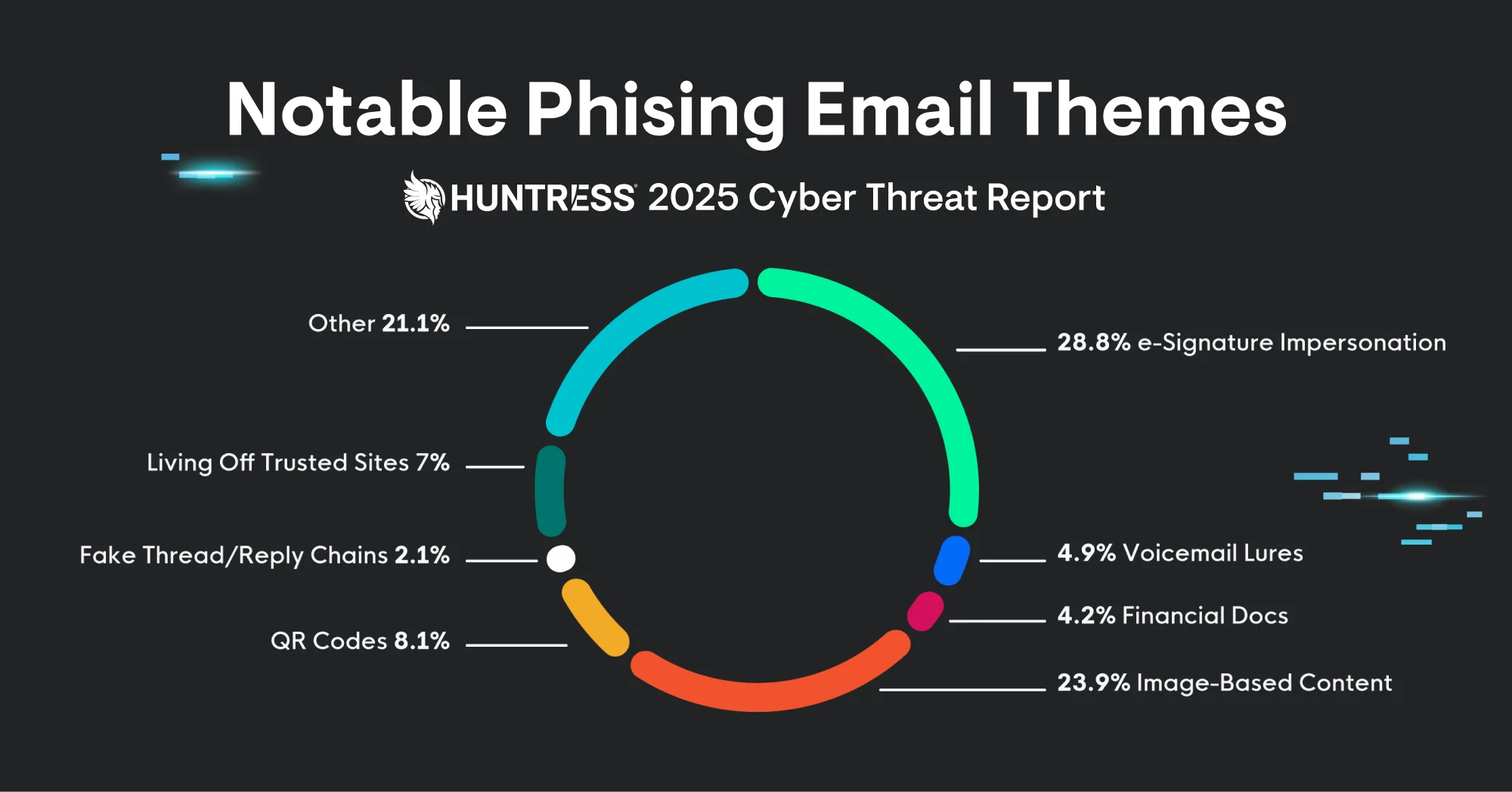
Back then, phishing emails were usually filled with broken English, pixelated logos, and outrageous promises. They cast wide nets, hoping to catch the most vulnerable users. While some people fell for these obvious scams, most recipients could clock them a mile away.
Today's modern phishing tactics
Fast-forward to today, and the phishing landscape has transformed dramatically. Cybercriminals now use AI-powered tools to craft grammatically perfect emails that mirror legitimate communications. They study company communication styles, replicate exact formatting, and even time their attacks to coincide with regular business activities.
Modern phishing attempts often target specific individuals or organizations (known as spear phishing). Attackers research their victims on social media, company websites, and professional networks to create highly personalized messages. They might reference recent company news, mutual connections, or industry-specific words and phrases to build credibility.
These sophisticated attacks can fool even the most savvy internet users. The key difference lies in the details—subtle inconsistencies that become apparent when you know what to look for.
Beyond email – new phishing channels
Phishing has expanded beyond traditional email to include multiple attack vectors. QR code phishing (or "quishing") has surged in popularity, with attackers embedding malicious links in seemingly innocent QR codes. Victims scan the code expecting legitimate content but land on credential-stealing websites.
SMS phishing, or "smishing," targets mobile users with fake text messages claiming urgent account issues or prize notifications. Social media platforms have become hunting grounds for phishers who create fake profiles to impersonate trusted people and brands.
These multi-channel approaches make detection more challenging, so users have to stay vigilant across all digital communications.