A Deep Dive Into One of Cybersecurity’s Most Notorious Malware Frameworks
Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and dangerous with each iteration. TrickBot, an infamous malware framework, is one of the most resilient and notorious examples in the cybersecurity landscape. What started as a relatively simple banking trojan has transformed into a versatile and modular platform, capable of enabling devastating ransomware attacks and providing a formidable tool for cybercriminals.
This deep-dive explores what TrickBot is, how it operates, and why it still poses a significant threat to organizations even after takedown efforts. By the end of this guide, you’ll understand TrickBot’s history, capabilities, and infection strategies, along with actionable defenses to protect your systems.
What is TrickBot
TrickBot originally emerged in 2016 as a banking trojan designed to steal financial credentials. Over time, it has evolved into a modular malware framework, widely used as a loader for ransomware and various criminal payloads. Cybercriminals quickly recognized TrickBot’s adaptability and capability, which made it a centerpiece in many malware-as-a-service (MaaS) operations.
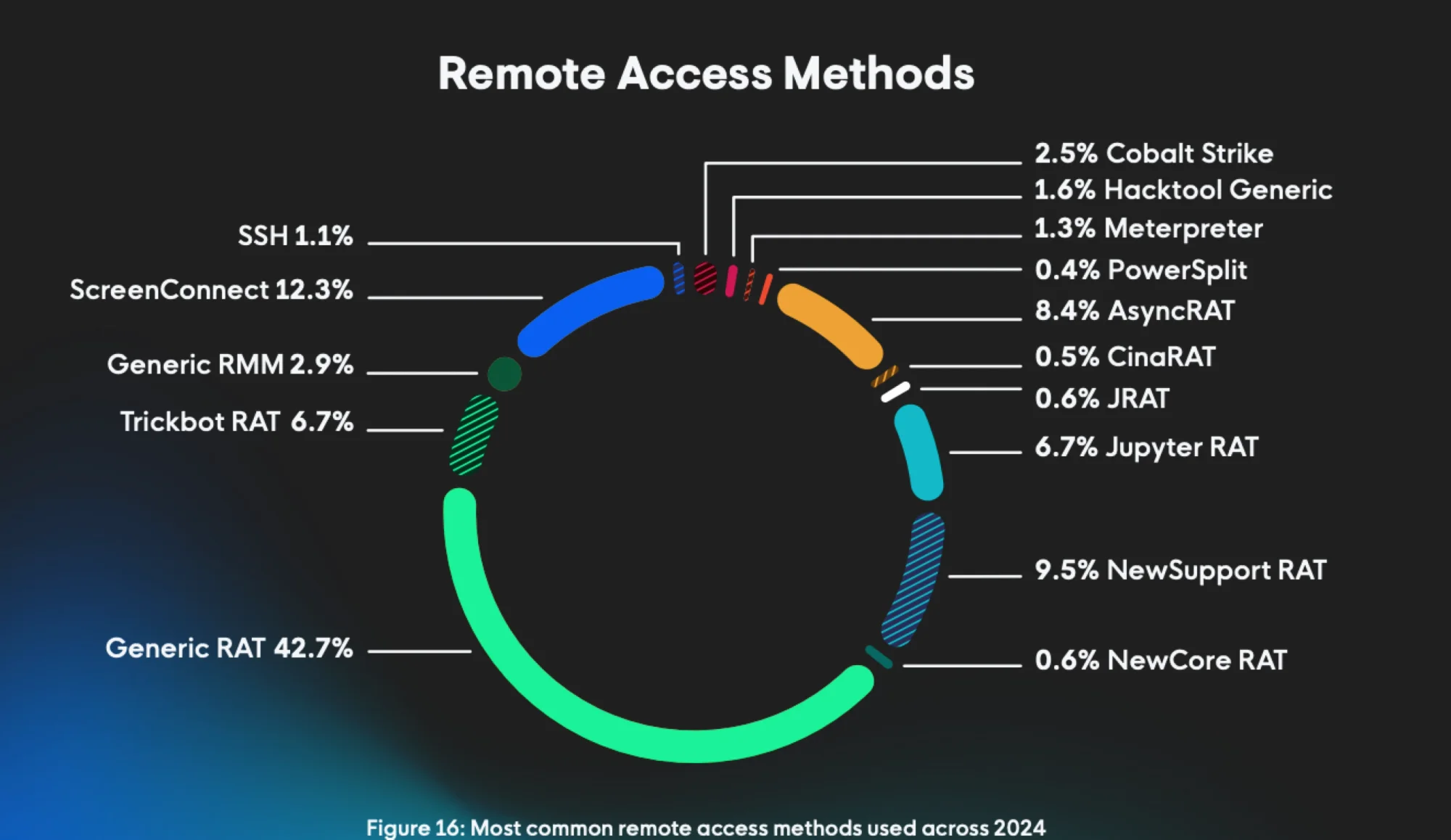
The Huntress 2025 Cyber Threat Report found that TrickBot is still being used by threat actors for remote access, with the malware accounting for 6.7 percent of the remote access methods used across 2024.
Figure 1: The Huntress Cyber Threat Report most common remote access methods
Key Characteristics of TrickBot:
Modular Architecture
TrickBot’s functions are split into separate modules, allowing attackers to deploy flexible combinations of tools depending on their goals, such as data theft, lateral movement, or ransomware delivery.
Financial Theft Origins
Initially, TrickBot targeted banking credentials by injecting malicious code into a victim's browser during financial transactions.
Ransomware Enablement
Over the years, TrickBot became a key element in delivering ransomware payloads, partnering with strains like Ryuk and Conti.
Crimeware as a Service
TrickBot has been offered as a service to other cybercriminal groups, making it a major player within botnet infrastructure and MaaS operations.
TrickBot became a staple in the arsenal of cybercriminal entities like WIZARD SPIDER, continually evolving to keep its operations relevant.
TrickBot Capabilities and Modules
TrickBot’s modular nature is the key to its success. By loading modules on an as-needed basis, attackers can adapt the malware for specific objectives, ranging from initial reconnaissance to full-scale ransomware operations.
Essential TrickBot Modules:
Credential Stealer
Harvests credentials stored in browsers, email clients like Outlook, and Windows Vault.
Web Injects
Used to carry out banking fraud by injecting malicious code into online banking sessions.
Network Reconnaissance
Scans compromised networks, mapping out systems to facilitate lateral movement.
Remote Desktop Capabilities
Enables attackers to gain VNC access for direct control over infected endpoints.
Loader for Ransomware
TrickBot has acted as a loader for high-profile ransomware strains like Ryuk and Conti.
Persistence Mechanisms
TrickBot ensures it remains in the environment by using tools like scheduled tasks and registry modifications.
These capabilities make TrickBot not only a security threat but also a critical red flag of deeper compromise when detected.
How TrickBot Infects Systems
TrickBot employs numerous methods to infiltrate systems. Here are the most common attack vectors and techniques:
Common Infection Vectors
Phishing Emails: A classic tactic, where emails containing malicious attachments or links trick victims into enabling macros, leading to the execution of TrickBot malware.
Fake Software Updates: TrickBot disguises itself as legitimate software installers or updates, gaining the victim’s trust.
Secondary Payloads: TrickBot is often dropped by other notorious malware like Emotet as part of multi-stage attacks.
Exploitation Techniques
PowerShell and WMI Abuse: TrickBot uses PowerShell scripts and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) to deploy malicious code.
Living-off-the-Land Binaries (LOLBins): The malware leverages built-in tools like mshta.exe or certutil.exe for malicious activities, evading detection.
Understanding these vectors can help organizations strengthen their defenses against this resilient malware.
TrickBot Lifecycle and Advanced Attacks
TrickBot’s lifecycle generally follows a well-defined attack chain, often leading to ransomware deployment. Here’s how it typically works:
Gained through phishing, malicious downloads, or as a dropper by malware like Emotet.
Privilege Escalation
Exploits vulnerabilities to gain higher-level account permissions.
Lateral Movement
Scans the network for valuable assets and spreads to other systems using protocols like SMB.
Post-Exploitation Tools
Deploys tools like Mimikatz for credential theft or other software to disable defenses.
Ransomware Delivery
Acts as a loader for ransomware like Ryuk or Conti, causing disruptions and financial damage.
Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK Framework
TrickBot’s various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) align closely with MITRE ATT&CK, making it a valuable resource for defenders to understand its behavior.
TrickBot Takedown Attempts and Current Status
Cybersecurity leaders have made several attempts to disrupt TrickBot operations. One of the most notable efforts occurred in 2020, led by Microsoft and the FS-ISAC, which successfully dismantled TrickBot’s infrastructure. While this disrupted its activities temporarily, TrickBot operators adapted quickly, rebuilding their capabilities under different botnet ecosystems.
Did TrickBot Survive?
Yes. Some of TrickBot’s operators were even absorbed into groups behind ransomware strains like Conti, showing that, despite takedowns, the malware framework’s legacy lives on in various forms.
Defending Against TrickBot
Defending against TrickBot involves a comprehensive approach that combines technology, training, and proactive measures.
Actionable Defenses
Use tools with behavioral analysis to detect and block TrickBot’s techniques in real-time.
Enhance Email Security
Phishing emails are a primary vector. Ensure robust email filtering and user education on spotting malicious links or attachments.
Regular Patching
TrickBot exploits known vulnerabilities. Keep systems, software, and devices updated to close potential entry points.
Monitor for IOCs
Continuously scan systems for TrickBot’s Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and unusual network behavior.
Incident Response Planning
Be prepared to respond with isolation and remediation to minimize damage if TrickBot is detected in your network.
Taking these steps can significantly reduce the risk of TrickBot infections and their devastating consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
TrickBot started as a sneaky banking trojan but quickly leveled up into a modular malware powerhouse. These days, it’s a favorite tool for cybercriminals to pull off credential theft, lateral moves inside networks, and deploying nasty payloads like Ryuk or Conti ransomware. Think of it as a Swiss Army knife—but for hackers.
TrickBot gets around faster than bad gossip, using methods like these:
- Phishing emails: Weaponized attachments and macros are its bread and butter.
- Compromised websites: Triggering drive-by downloads.
- Piggybacking on other malware: Bad actors like Emotet and QakBot drop TrickBot as a secondary payload.
Once inside, it plays dirty with stealthy tools like PowerShell and WMI to dig deeper into systems while staying off your radar.
TrickBot doesn’t discriminate when it comes to data theft. Here's what it’s after:
- Online banking info and credentials
- Browser-stored passwords and autofill data
- Email login info (Outlook lovers, beware)
- Sensitive data from Active Directory and network maps
- Cryptocurrency wallets and SSH keys (depending on the module it uses)
Bottom line? If it’s valuable, TrickBot wants it.
You bet it is. While a partial takedown in 2020 slowed it down, TrickBot dusted itself off and found a way to keep causing trouble. It’s now operating through revamped botnets and ransomware-as-a-service gangs like Conti. Cybercriminals don’t quit easily, which is why TrickBot remains a persistent headache for organizations.
They might be besties in the malware world, but they play different roles in the attack chain.
- Emotet: Think of it as the party starter, infecting systems via phishing and teeing up TrickBot for the real heist.
- TrickBot: The brains of the operation, doing reconnaissance, stealing credentials, and setting the stage for ransomware.
Together, they’re a tag team you don’t want messing with your network.
Good news: You’re not powerless. Here’s how to stay ahead of TrickBot’s antics:
- Train employees to spot phishing attempts and filter malicious emails like a pro.
- Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools with behavior-based detection.
- Limit access to privileged accounts with strict “least privilege” policies.
- Keep software updated and disable macros in Office docs (seriously, just do it).
- Monitor for known Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and watch for lateral movement.
Think of these steps as your TrickBot battle plan.
TrickBot has teamed up with some notorious ransomware gangs over the years, including:
- Ryuk
- Conti
- Maze (back in the day)
These attacks usually follow the same pattern: TrickBot breaks in, does the dirty work (like network mapping and data theft), and then drops ransomware to lock down your systems.
Stay sharp, stay vigilant, and don't give TrickBot or its pals a way in.


Why TrickBot Remains a Major Threat
Despite numerous takedown efforts, TrickBot’s modularity, resilience, and integration into major ransomware operations make it a persistent threat. Its capacity to evolve and adapt to different targets ensures that it remains relevant in the cybersecurity landscape.
Organizations that detect TrickBot in their environment should treat it as a serious indicator of compromise (IOC) and take immediate action to investigate and remediate their systems.


Protect What Matters