Living Off the Land (LOTL) attacks are a type of cyberattack where threat actors use legitimate, trusted tools and software already present on a target system to carry out malicious activities. Instead of bringing their own malware, attackers exploit built-in system utilities, administrative tools, and legitimate applications to avoid detection and achieve their objectives.
Key Takeaways
By the end of this article, you'll understand:
The definition and core concepts of Living Off the Land (LOTL) attacks
Common tactics and legitimate tools used in LOTL attacks
Why these attacks are particularly difficult to detect and defend against
Proven strategies and best practices for defending against LOTL techniques
How security solutions like Huntress help protect organizations from these stealthy threats
Understanding LOTL Attacks
Think of LOTL attacks like a burglar using your own house key instead of breaking a window. Cybercriminals have figured out that using legitimate system tools is way smarter than dragging suspicious malware into your network. Why set off alarms when you can walk right through the front door?
These attacks get their name from the military concept of "living off the land"—using local resources instead of bringing your own supplies. In cybersecurity, this means attackers use PowerShell, Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), legitimate administrative tools, and even applications like Microsoft Teams to accomplish their goals. These are often referred to as LOLBins (living off the land binaries)
The scary part? To most security systems, these activities look completely normal. When PowerShell runs a script, your antivirus doesn't immediately think "cyberattack"—it thinks "legitimate administrative task."
Common LOTL Tools and Techniques
Windows Environment Tools
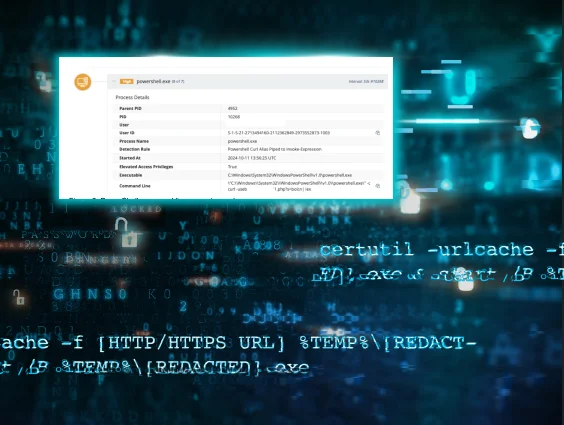
PowerShell is probably the most popular tool in an attacker's LOTL toolkit. This powerful command-line interface can download files, execute commands, and move laterally through networks—all while looking like routine system administration.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) lets attackers query system information, execute commands remotely, and maintain persistence. Since WMI is essential for legitimate system management, blocking it entirely isn't an option for most organizations.
Built-in Windows utilities like certutil.exe, bitsadmin.exe, and regsvr32.exe can be weaponized to download malicious payloads, maintain persistence, or execute code in ways their original developers never intended.
Linux and Unix Systems
The GTFOBins project catalogs how common Unix binaries can be exploited. Tools like cp, cat, and netcat—which system administrators use daily—can be turned into attack vectors.
Signed Drivers and Applications
The LOLDrivers project tracks legitimate, signed Windows drivers that contain vulnerabilities or can be abused for malicious purposes. Since these drivers have valid digital signatures, they can bypass many security controls designed to block unsigned code.
Why LOTL Attacks Are So Effective
Stealth and Evasion
Traditional security tools look for known malware signatures and suspicious file behaviors. LOTL attacks flip this approach on its head by using tools that are supposed to be there. When Microsoft Teams spawns a child process, most automated systems think "legitimate business application," not "potential security threat."
Reduced Attack Surface Detection
Because attackers aren't introducing new files or executables, there's less evidence for security teams to find. The attack artifacts blend into normal system activity, making forensic analysis significantly more challenging. Reducing your organization’s attack surfaces by following our best practices helps mitigate your cyber risk.
Living in Plain Sight
According to research from security firms, LOTL techniques are involved in over 70% of successful breaches. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has specifically warned about the increasing use of living-off-the-land techniques in targeted attacks against critical infrastructure.
Defense Strategies Against LOTL Attacks
Behavioral Analysis and Monitoring
Instead of just looking for bad files, focus on unusual behaviors. Monitor for:
PowerShell executions with suspicious parameters
Unusual network connections from system utilities
Administrative tools running in unexpected contexts
Abnormal process relationships and command chains
Application Control and Whitelisting
Implement strict controls on how legitimate tools can be used:
Restrict PowerShell execution policies
Limit which users can run administrative utilities
Monitor and log all usage of high-risk legitimate tools
Use AppLocker or similar technologies to control script execution
Enhanced Logging and Visibility
Enable comprehensive logging for:
PowerShell script block logging
WMI activity monitoring
Process creation events
Network connections from system processes
Command-line arguments for all processes
Threat Hunting and Analysis
Proactively search for signs of LOTL activity:
Look for unusual patterns in legitimate tool usage
Analyze command-line arguments for suspicious parameters
Monitor for tools being used outside their normal operational context
Track lateral movement patterns using built-in utilities
How Huntress Protects Against LOTL Attacks
Huntress specializes in detecting the subtle signs of LOTL attacks that traditional security tools often miss. Our human-driven threat hunting approach combines advanced behavioral analysis with expert security analysts who understand how legitimate tools can be weaponized.
Our platform continuously monitors for suspicious use of built-in utilities, tracks unusual process behaviors, and identifies the telltale signs of living-off-the-land techniques. When automated systems see "normal" activity, our team of security experts looks deeper to spot the abnormal patterns that indicate a potential breach.
Staying Ahead of Stealthy Threats
LOTL attacks represent a fundamental shift in how cybercriminals operate. By using the tools already in your environment, they've found a way to hide in plain sight. The key to defense isn't just better technology—it's a better understanding of how legitimate tools can be misused and implementing monitoring that focuses on behaviors rather than just files.
The cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, and so do the tactics of threat actors. Understanding LOTL techniques and implementing appropriate defenses is essential for any organization serious about protecting their digital assets.
Ready to strengthen your defenses against these stealthy attacks? Discover how Huntress can help your organization detect and respond to living-off-the-land techniques before they become full-scale breaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Traditional malware brings new, malicious files into your system. LOTL attacks use tools that are already there and supposed to be there, making them much harder to detect with signature-based security solutions.
Traditional antivirus solutions struggle with LOTL attacks because they rely on identifying malicious files and signatures. Since LOTL attacks use legitimate tools, behavioral analysis and advanced threat detection are more effective.
PowerShell is frequently cited as the most abused legitimate tool, due to its powerful capabilities for system administration, network access, and script execution.
No, LOTL attacks affect all operating systems. Linux and Unix systems face similar threats through abuse of built-in utilities, though the specific tools and techniques may differ.
Small businesses should focus on basic security hygiene: enable comprehensive logging, restrict administrative tool access, implement user training, and consider managed security services that specialize in behavioral threat detection.




Protect What Matters